Last Updated on: 19th September 2024, 02:56 pm
Coffee is more than just a beverage; it’s a global phenomenon that weaves itself into the very fabric of daily life in many cultures. As we look towards 2024, we aim to highlight the Best Countries for Coffee, showcasing regions renowned for their unique coffee production, diverse coffee beans, and rich coffee culture. From the vast fields of Brazil, which produces over 2.6 million metric tons of coffee annually, to Colombia’s focus on high-quality Arabica beans, these countries not only provide the world with excellent coffee but also embody a spirit of sustainability and ethical consumption that is increasingly vital to global coffee lovers12. In this article, we’ll explore the characteristics that make these countries stand out, aiming to guide consumers in their choices and enhance their appreciation of coffee harvesting and the quality of beans they choose.
Key Takeaways
- Brazil excels in coffee production, contributing significantly to the global coffee market.
- Colombia is renowned for its high-quality Arabica beans, accounting for almost 9% of global exports.
- Increasing demand for ethically sourced coffee shapes sustainable cultivation practices.
- Global coffee culture encompasses diverse brewing methods, enhancing consumer experiences.
- Countries like Vietnam and Indonesia stand out as leaders in robusta coffee production.
Coffee Production Around the Globe
Coffee production is a linchpin in the global agricultural landscape, with around 70 countries engaged in growing this beloved crop, and about 50 of these nations exporting their beans3.Coffee is the second most traded commodity, falling just behind oil in terms of trade volume3. The coffee-producing countries are primarily located in tropical regions between the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn.
Brazil stands out as the world’s largest coffee producer, generating an impressive 2.68 million metric tons annually, a position it has held for over 150 years4. Vietnam follows closely behind, exporting more than 1.5 million metric tons each year, and contributing significantly to the global Robusta bean output4. Colombia is renowned for its production of over 760 thousand metric tons of coffee, especially its aromatic Arabica beans, while Indonesia, with its diverse coffee flavors, contributes over 668 thousand metric tons annually4.
Interestingly, Ethiopia, regarded as the birthplace of coffee, produces in excess of 421 thousand metric tons annually, with most of its high-quality varieties being reserved for local consumption4. Other notable producers include Peru, Honduras, Guatemala, and Uganda, each contributing distinct flavors that showcase the rich traditions of coffee cultivation within their respective coffee regions4.
This extensive coffee landscape illustrates not only the vast strategies employed in coffee cultivation but also the pivotal role played by these nations in satisfying the world’s ever-growing demand. According to statistics, approximately 75-80% of people globally consume caffeine regularly5.
| Country | Coffee Production (Metric Tons) | Type of Coffee |
|---|---|---|
| Brazil | 2,680,515 | Primarily Arabica |
| Vietnam | 1,542,398 | Robusta |
| Colombia | 754,376 | Arabica |
| Indonesia | 668,677 | Diverse varieties |
| Honduras | 475,042 | Primarily Arabica |
| Ethiopia | 471,247 | Arabica |
| Peru | 346,466 | Arabica |
| India | 234,000 | Arabica and Robusta |
| Guatemala | 245,441 | Arabica |
| Uganda | 209,325 | Robusta |
The Rich History of Coffee Cultivation

Coffee cultivation traces its origins back to Ethiopia, often celebrated as the birthplace of this beloved beverage. By the 15th century, coffee was being cultivated in the Yemeni district of Arabia. Its popularity spread rapidly, reaching Persia, Egypt, Syria, and Turkey by the 16th century6. The journey continued with the establishment of coffee houses, with the first European one opening in Constantinople in 14757.
As coffee made its way into Europe, it found a receptive audience. England embraced coffee in 1651, marked by the opening of the first coffee house in Oxford. France followed suit in 1669 when Suleyman Aga introduced coffee to Paris7. This enthusiasm led to the proliferation of coffee houses, with over 300 established in London by the mid-17th century6.
In North America, coffee gained traction after a boycott of tea, particularly following the events of the Boston Tea Party in 1773, which shifted public preference towards coffee. The first legal coffee retailer in Boston, Dorothy Jones, received her license in 16707. By the early 18th century, coffee cultivation expanded into Central America, with significant coffee harvests reported in 17267.
Latin American countries rose to prominence as top coffee producers by the mid-18th century. Brazil emerged as the world’s largest producer, significantly shaping global coffee markets8. Today, Brazil remains a dominant force in coffee cultivation, famous for both Arabica and Robusta varieties. Other notable countries contributing to this rich history include Colombia, Guatemala, and Mexico, each offering unique flavor profiles and cultivation techniques8.
Best Countries For Coffee
The world of coffee is diverse, with numerous countries producing a wide range of unique flavors and beans. The Best Countries For Coffee showcase not only remarkable production volumes but also distinctive characteristics associated with their local coffee. Highlighting the Top Coffee Producing Nations, we delve into the countries renowned for their high-quality coffee beans and the unique varieties they cultivate.
Top Coffee Producing Nations
Brazil stands out as the largest coffee-producing country globally, exporting around one-third of the world’s total coffee9. In fact, during the 1920s, Brazil contributed to nearly 80% of coffee supplies worldwide10. Following Brazil, Vietnam ranks as the second-largest producer, largely focusing on robusta coffee due to its favorable growing conditions. Colombia follows closely as the third-largest producer, offering exceptional Colombian Arabica beans, known for their sweet and fruity profile9.
African nations like Ethiopia and Uganda play a pivotal role too, as they account for 62% of sub-Saharan coffee production9. Likewise, countries such as Costa Rica are recognized for their commitment to high-quality coffee, which often ranks among the best in the world10.
Unique Coffee Varieties by Country
The appeal of coffee is enhanced by the Unique Coffee Varieties found in various nations. For instance, Indonesia offers coffee grown on volcanic soil, resulting in a rich and earthy flavor profile complemented by spice notes. Only one-fifth of its production consists of arabica, with robusta taking the lead in export volumes9.
Packed with ideal climate conditions, Panama’s coffee beans are frequently seen as some of the finest globally10. Furthermore, Ethiopia is celebrated for producing heirloom varieties, which present a complexity of flavors cherished by coffee enthusiasts. Each country’s distinct growing environment contributes to the wide array of flavors found in coffee beans worldwide.
Understanding Coffee Quality Standards

The world of coffee is deeply influenced by its quality standards, which shape consumer preferences and production practices. A significant 64 percent of Americans drink coffee every day, illustrating the high demand for quality in the U.S. market11. Quality assessment begins with grading systems that are inherently fragmented; each coffee-producing country has its own criteria without a universal standard12.
Key factors in determining Coffee Quality include screen size, altitude, bean variety, and defect counts. For instance, the SCA Green Arabica Classification System (GACCS) allows for assessing primary and secondary defects in coffee beans12. This system is particularly vital for producers striving to meet international Coffee Standards, ensuring the beans maintain high quality even amidst challenges like varying weather conditions.
The allure of coffee extends further when considering the top coffee-producing nations. For example, Colombia is the second-largest coffee producer globally, with an output of 13-17 million bags annually11. Brazil tops this list, consistently delivering high volumes of coffee while regions like Hawaii produce much less, at only 40-45,000 bags per year, making their shipments particularly scarce and valuable11.
Different nations produce unique varieties that contribute to the overall perception of quality. Ethiopia, renowned for being the birthplace of arabica beans, is revered in Best Countries For Coffee lists due to its rich history and vibrant flavor profiles11. As consumers become increasingly discerning, the emphasis on quality continues to evolve, shaping how coffee is grown, processed, and presented.
Best Coffee Regions and Their Specialties

Coffee lovers around the globe often seek the Best Coffee Regions to indulge in unique flavors and aromas. With a rich tapestry of coffee varieties, understanding the distinction between Arabica vs. Robusta can enhance appreciation for the diverse offerings of coffee specialties worldwide. From the high-altitude plantations of Colombia to the fertile fields of Brazil, each region contributes distinct characteristics to this beloved beverage.
Arabica vs. Robusta: What’s the Difference?
The two primary species of coffee beans, Arabica and Robusta, represent a significant portion of the coffee market. Arabica accounts for about 60-70% of global coffee production and is known for its sweet, soft taste and higher acidity. In contrast, Robusta is favored for its strong, bitter flavor and higher caffeine content, making it a popular choice for espresso blends. The choice between these two types can significantly influence a coffee drinker’s experience, highlighting regional flavors and local growing conditions.
Notable Coffee Zones Globally
Several regions stand out for their exceptional coffee production, each with its distinct specialties:
- Brazil: As the largest producer for over 150 years, Brazil offers nutty and sweet varieties with a full body, accounting for a significant portion of the world’s coffee market1314.
- Colombia: Known for its well-balanced flavor with caramel sweetness, Colombian coffee is cherished for its distinct profile14.
- Ethiopia: Considered the birthplace of coffee, Ethiopia presents fruity and wine-like coffees that vary by processing method, contributing to its unique taste14.
- Vietnam: The world’s second-largest coffee exporter, Vietnam specializes in producing Robusta coffee, known for its strong and bold flavors13.
- Indonesia: The Sumatra region is celebrated for its dark, bold coffees, featuring a unique smoky and earthy quality14.
- Laos: Recognized for its special Arabica coffee with light citrusy and floral notes, along with higher-altitude Robusta13.
Coffee Culture: A Global Phenomenon
Coffee culture varies significantly from country to country, reflecting unique traditions that define coffee consumption practices. In Italy, enjoying espresso in small concentrated shots at local cafes embodies a distinctive ritual, showcasing the significance of quick social interactions15. Ethiopia’s traditional coffee ceremony highlights a communal experience, where coffee is freshly roasted, ground, and brewed in a clay pot15. Meanwhile, Turkish coffee is characterized by its finely ground beans and strong flavor, served in small cups, allowing for meaningful gatherings15. Coffee culture serves as a global thread, connecting millions through shared experiences, art, and diverse brewing methods.
Traditions in Coffee Consumption
Regions around the world enjoy different facets of coffee culture. In Sweden, the tradition of fika emphasizes relaxation and connection over coffee and pastries, while France’s elegant espresso culture radiates sophistication15. The Japanese focus on precision and quality in specialty coffee preparation reflects their cultural emphasis on detailed craftsmanship15. These traditions not only enrich local coffee experiences but also foster a sense of community across diverse cultures.
The Impact of Coffee on Local Economies
The coffee industry is an economic powerhouse, worth billions of dollars globally and employed millions of people16 Coffee is grown in over 70 countries and is one of the most traded commodities, creating vast networks that support farmers and local businesses1617. Notably, Starbucks and Nescafé have become pivotal brands influencing coffee culture and economics worldwide17. Rising coffee prices pose challenges for affordability but simultaneously ignite opportunities for entrepreneurs eager to innovate and expand within coffee markets16. Overall, coffee remains a vital catalyst for economic growth and community development across nations.
Top Coffee Exports by Country

The coffee industry continues to thrive, with various countries playing pivotal roles in coffee exports globally. In 2024, Brazil maintains its status as the leading coffee exporter, supplying approximately 2.6 million metric tons annually, with 70% of its production being Arabica beans18. Following Brazil, Vietnam stands out with its robust production of 1.54 million metric tons, primarily consisting of Robusta beans, significant for its Central Highlands cultivation19
Leading Coffee Exporters of 2024
As the dynamics of the coffee market evolve, the five largest coffee exporting countries—Brazil, Vietnam, Colombia, Germany, and Honduras—collectively comprise 42.8% of all global coffee exports20. Coffee is the second most traded commodity worldwide, behind oil, with around 50 countries actively participating in its export19. In 2023, Europe was the leading region concerning coffee export value, amounting to $16.2 billion20. With a total of 8.46 million tons of coffee exported globally, the market has seen intriguing trends, including Colombia producing 754,376 metric tons and Indonesia closely following1918.
How Export Trends Affect Local Markets
The fluctuations in coffee export trends directly influence local markets and farmers’ livelihoods. For instance, while Brazil experienced a positive net export surplus of $7.2 billion in 2023, Colombia, Indonesia, and Ethiopia faced declines in coffee export sales during the same year20. Such variations could significantly impact farmers’ earnings and the overall economic stability of coffee-growing regions. The demand for coffee not only sustains local economies but also reflects the shifting preferences in consumer tastes globally19.
Ethics in Coffee Production
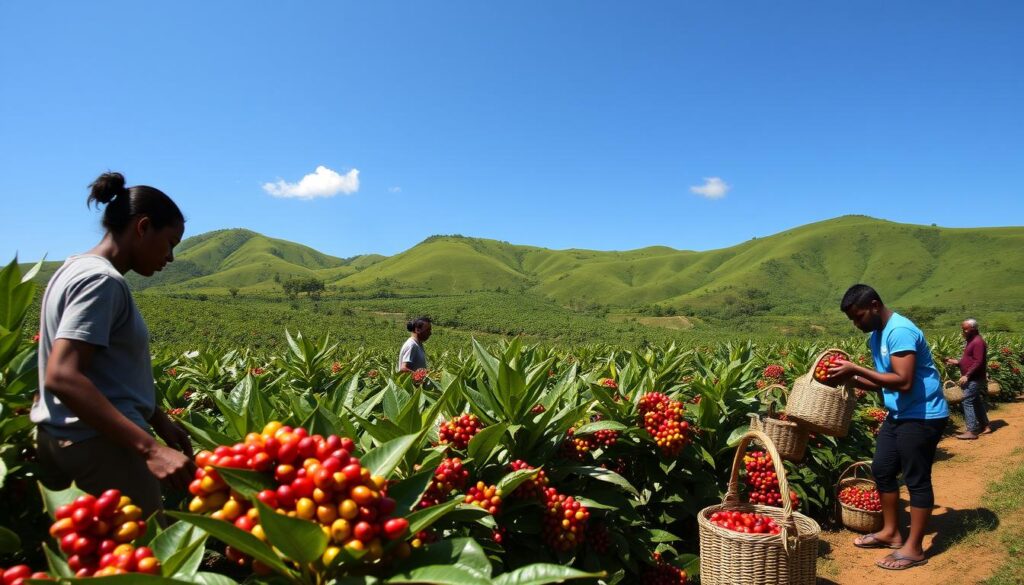

The coffee industry faces significant ethical issues regarding the treatment of farmers. Consumers often remain unaware of the challenges faced by coffee farmers, including low wages and inadequate working conditions. In many cases, small farmers struggle against the fluctuations in the global coffee market, receiving just pennies per pound for their beans21. The majority of these farmers reside in developing countries, while the primary consumers are located in North America and Europe22. Awareness of these issues is essential for fostering a more ethical approach to coffee consumption.
Challenges Faced by Coffee Farmers
The coffee cultivation landscape presents numerous challenges faced by coffee farmers. Climate change threatens yields and could render up to 50% of current coffee-growing lands unsuitable by 205021. Additionally, the dependence on fair trade certifications often highlights the precarious nature of their labor, as many farmers receive minimal compensation, making it difficult to sustain their livelihoods23. Women play a crucial role, contributing up to 70% of labor, yet they frequently encounter inequalities in resources and decision-making21.
Efforts Towards Sustainable Coffee Cultivation
To counter these challenges, various initiatives promote sustainable coffee cultivation. Companies like Bean & Bean actively support women-run farms, ensuring fair compensation and economic empowerment21. The rise of direct trade practices allows coffee farmers to establish personal connections with roasters, which can increase their earnings and enforce more ethical sourcing practices23. Furthermore, certifications, such as Fair Trade and organic labels, not only protect the environment but also ensure that farmers are paid a fair price for their beans, fostering overall well-being23.
To make a meaningful impact, consumers need to be informed and supportive of ethical practices in coffee production. Engaging with companies committed to sustainability while choosing certified products can resonate throughout the coffee supply chain, resulting in improved conditions for farmers globally and better ethical consumption.
Conclusion
As we explore the best countries for coffee, it becomes clear that the significance of reputable sources cannot be overstated. Nations like Colombia, Brazil, Ethiopia, and Kenya stand out not only for their quality coffee production but also for their rich coffee culture. For instance, Colombia is celebrated for its bright acidity and fruity notes, while Ethiopia offers a unique experience that many enthusiasts cherish24.
Furthermore, the trends observed in recent years highlight a notable shift towards more innovative processing methods, such as Anaerobic processing, which has been making waves in competitions like the Cup of Excellence. The findings reveal a growing appreciation for unique varietals, particularly the Gesha, which has dominated awards for its exceptional scoring25. This interconnectedness of high-quality coffee production and cultural importance lays a foundation for consumers to be more mindful of their choices.
Looking ahead, it is crucial to support sustainable practices that benefit coffee farmers and preserve the unique characteristics of their regions. By choosing ethically sourced coffee and exploring the rich diversity in flavors, coffee lovers can make informed selections that honor the craft behind every cup. Ultimately, embracing this journey not only enhances our coffee experience but also fosters a more sustainable future for the best countries for coffee production26.
FAQ
What are the best countries for coffee production in 2024?
How does coffee quality differ among regions?
What ethical concerns surround coffee production?
What distinguishes Arabica from Robusta coffee beans?
Why is coffee culture important globally?
How do coffee exports impact local economies?
What are some unique coffee varieties produced by different countries?
How can I ensure I’m buying ethically sourced coffee?
Source Links
- https://finance.yahoo.com/news/15-countries-best-coffee-according-204231474.html
- https://farrerscoffee.co.uk/blogs/blog/top-10-coffee-producing-countries-around-the-world?srsltid=AfmBOooHx_6Aizdycvb7ARXaRPntia9MLHHAkd-kEeKRJEemrWxBZ7VB
- https://farrerscoffee.co.uk/blogs/blog/top-10-coffee-producing-countries-around-the-world?srsltid=AfmBOopR-caPOEiGdo5OOKvzT3DzuLnnFnVDNzWFwzPJM2k6SrcJOu9p
- https://www.nescafe.com/gb/coffee-culture/knowledge/coffee-producing-countries
- https://fathomcoffee.com/coffee-regions-guide/
- https://www.ncausa.org/About-Coffee/History-of-Coffee
- https://www.nescafe.com/in/understanding-coffee/coffee-history
- https://www.ncausa.org/about-coffee/coffee-around-the-world
- https://thestudio.coffee/countries-with-the-best-coffee/
- https://medium.com/@encover.co/question-answered-which-countries-make-the-best-coffee-15a5913ee854
- https://www.ictcoffee.com/news/best-coffee-beans/
- https://www.trabocca.com/coffee-knowledge/quality/coffee-grades-understanding-the-basics/
- https://halo.coffee/blogs/discover/coffee-regions-a-quick-guide-to-coffee-growing-regions
- https://perkcoffee.co/my/coffee-regions-and-their-different-flavour-profiles/
- https://www.nationwidecoffee.co.uk/news/coffee-culture-around-the-world-a-journey-through-global-coffee-traditions
- https://winwin.coffee/blog/the-coffee-culture-a-global-phenomenon
- https://aerialresupplycoffee.com/blogs/the-resupply-blog/the-history-of-good-coffee-how-it-became-a-global-phenomenon?srsltid=AfmBOop7Iyl53B6cROrupEzQXrWkK_YypeM-AXMiLb-qBUBg5m47CFX_
- https://henryshouseofcoffee.com/blogs/blog/top-5-coffee-producers-in-the-world?srsltid=AfmBOopdp7xlOORuXzGKHUkgMVFqi9m_9xY9ZCsyxTdKfGS9lpiNeK_N
- https://farrerscoffee.co.uk/blogs/blog/top-10-coffee-producing-countries-around-the-world?srsltid=AfmBOorHKxuIk5LPEV2feCc4ukI6NUtEinexFbCCU6APtVNL2YZl_K9W
- https://www.worldstopexports.com/coffee-exports-country/
- https://beannbeancoffee.com/blogs/beansider/what-are-the-ethical-issues-of-coffee?srsltid=AfmBOoqex9oY2B5lAFgm9BVpe-GKmz765majIbgyUSFj2x_ne5h2no5h
- https://sustainability.wustl.edu/new-resource-provides-options-for-sustainable-and-ethical-coffee/
- https://www.haymancoffee.com/blogs/coffee-blog/sustainability-importance-ethical-coffee-bean-practices?srsltid=AfmBOor9GdAoN2pHNASKjGhxSvcC_Wr8oq9aPcslvaf_E98axC0g_MoF
- https://medium.com/@SteveSpring/discovering-coffee-origins-where-does-the-best-coffee-come-from-e0e66d7cf937
- https://coffeebros.com/blogs/coffee/what-country-has-the-best-tasting-coffee?srsltid=AfmBOop3Yo2QKJ-EdI9ymYh8vvkRRipZ1TSKm7xW0grrPQzjJTGPcsCb
- https://coffeechronicler.com/best-coffee-beans/

As a passionate, global-thinking Real Estate Investor I am constantly looking for the best opportunities to invest in Properties. With Aparthotel.com I am building an All-In-One Global Real Estate Platform, where people can analyse, rent or invest in properties. Additionally I help Investors with comparing the best financing options as well as give detailed Consultation on the buying process for Real Estate Investments around the world. I am looking forward to sharing my knowledge on this Website and feel free to reach out to me if you have any questions.

Comments